Latest news
The latest news about Biomass Research
Positive impacts of biodigesters
Biodigester technology is transforming lives in developing countries. It improves access to energy, stimulates soil health, and boosts rural livelihoods in many countries around the world. Key impacts include: renewable energy access through biogas for cooking, lighting, and productive uses; fertiliser (bioslurry) production that improves yields, soil health, and reduces reliance on synthetic fertilisers.
Other major advantages are time savings for women and children – no (less) need for fuelwood collection, health benefits from reduced indoor air pollution, avoided deforestation and reduced greenhouse gas emissions (2–8 tons CO₂ equivalent per 6 m³ biodigester/year). Additional economic gains often are realised from savings on energy and fertilisers plus income generation from boslurry or compost production. In some cases, carbon credits provide an additional source of income. At the regional and national levels, jobs are created through training and employment for masons and biodigester enterprises.
Read more in a report written by SNV in the Organic Fertilizer Valorization Implementer (OFVI) project: http://www.ofvi-abc.nl/reports.
Quick tests for bioslurry analysis in Mali
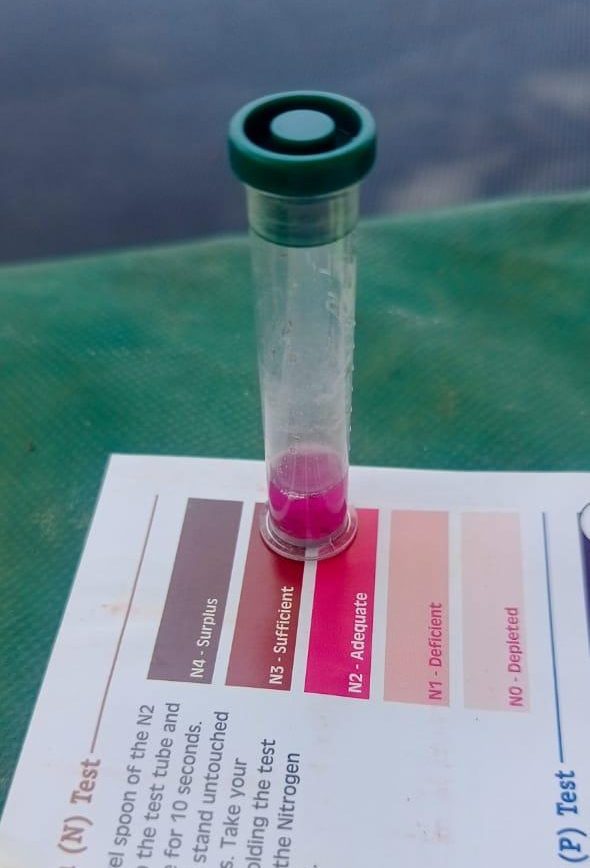
We have handed a set of nutrient quick tests to Moussa, a biodigester owner in Mali, as part of our ongoing research into the composition of bioslurry. Moussa will use the tests to measure key parameters such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and pH in the bioslurry produced by his system. These indicators are vital for assessing the agronomic value of bioslurry when used as a fertilizer in smallholder farming systems.
If you have data on the composition of bioslurry, compost, or bioslurry-enriched compost, we invite you to contribute to this effort by filling out the survey here : Survey Link
Stay tuned for updates on the Biomass Research website : https://biomassresearch.eu/news/
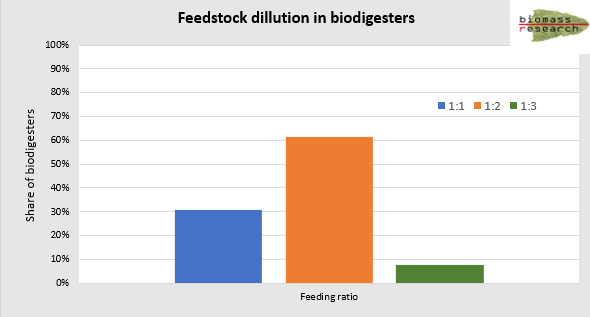
Biodigester feeding : Survey update on dilution ratio
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a vital renewable energy source that converts organic waste into biogas through natural microbial processes. This sustainable technology helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, manage waste efficiently, and produce clean energy for electricity, heating, and transportation. AD is used globally in agriculture, industry, and municipalities, supporting circular economies and energy security. AD is widely adopted across agriculture, industry, and municipal sectors, supporting both circular economies and energy security. Its global use is steadily increasing as a reliable and scalable sustainable energy solution.
Proper feedstock management is essential for the effective functioning of the biodigesters. The performance, stability, and gas yield of a biodigester are highly dependent on what goes into it and how it’s managed. Factors such as the type of organic material, its dilution ratio, and feeding frequency all impact the microbial processes inside the digester.
To better understand current feeding and operational practices, we are developing an inventory of biodigester feeding and management through a dedicated survey. Initial results have revealed something quite unexpected: while most scientific literature recommends a standard 1:1 feedstock-to-water dilution ratio, our survey indicates that a majority of users are actually using a 1:2 ratio. This opens up new avenues for research and practical optimization in this field.
We are continuing to gather more data and invite you to contribute by filling out the survey at the link below. Your input is valuable in shaping a clearer understanding of real-world biodigester practices.
More results will be presented in the future. Stay tuned for updates on the Biomass Research website : https://biomassresearch.eu/news/
Biomass Research joins TU Delft project to develop circular biowaste loop
A new TU Delft-led consortium, ABEL (Ab-initio Biowaste Loop), has received €6.7 million from the Dutch Research Agenda (NWA) to develop innovative technologies that convert low-grade organic waste into durable, sustainable materials that can be easily recycled at the end of their life. The project aims to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower emissions, and strengthen the Dutch bioeconomy. Biomass Research is proud to be part of this project, where it will contribute to the inventory of relevant data sources, spatial mapping of biomass availability, and characterization of residual biomass streams.
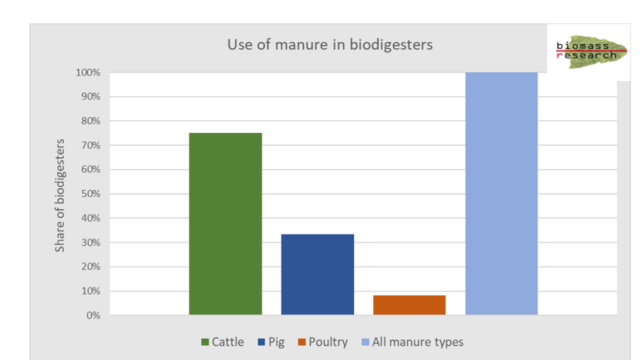
Biodigester feeding : Preliminary survey results
The initial results from our ongoing survey show that all biodigester owners use manure, with cow manure being the primary feedstock. The second major feedstock is pig manure.
We invite you to fill the survey in the link : Survey link
More results will be presented in the future. We will share updates on the Biomass Research website : https://biomassresearch.eu/news/
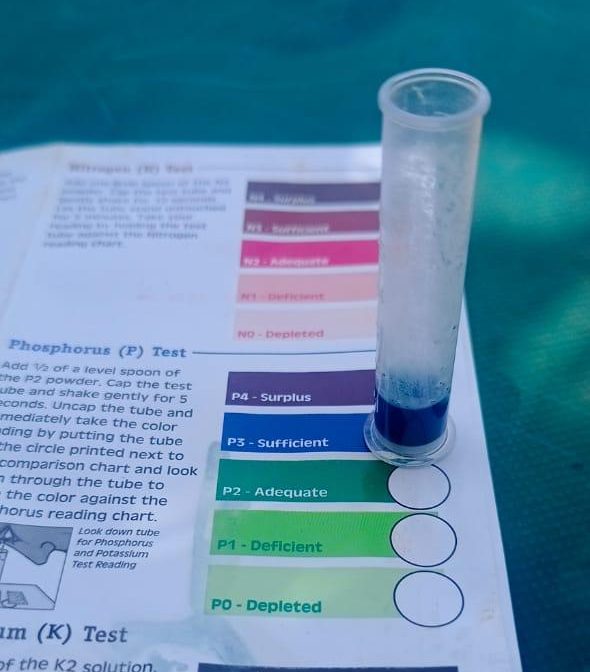
Quick tests help to determine nutrient concentrations
While markets for bioslurry (digestate) and compost made with bioslurry (Bioslurry Enriched Compost or BEC) are developing, there is an urgent need to obtain accurate information on the amount of nutrients that they contain. Biomass Research is leading the search for tests that are reliable, transparent, affordable, and easy to use. A recent evaluation of a quick test kit in Niger by Moussa Fofana (of DIBcoop) in the Organic Fertilizer Valorization Implementer (OFVI-ABC) project revealed promising results for both bioslurry and enriched BEC. The test focused on two essential nutrients – nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), two key nutrients for crop growth.
Key Findings:
BEC: The compost tested showed sufficient phosphorus and adequate nitrogen levels.
Bio-Slurry: Results indicated sufficient phosphorus, while nitrogen ranged between adequate and sufficient.
These results highlight the value of bioslurry and BEC as effective organic soil amendments. Their nutrient content supports healthy crop production and offers a practical alternative to chemical fertilizers, contributing to healthier farming systems.
Biomass Research Joins Dutch Trade Mission to Kenya
From March 17 to 20, Hans Langeveld, joined the Dutch trade mission to Kenya, fostering collaborations in sustainable agriculture and bio-based solutions.
Biomass Research has a huge track record in organic waste valorization, generating clean energy, producing cost-effective organic fertilizers, and improving soil health. During the mission, Hans engaged with key local stakeholders to explore innovative solutions for Kenya’s agricultural and bioenergy sector residue streams.
Kenya presents promising opportunities for collaboration. Biomass Research looks forward to sharing knowledge and developing projects that support environmental and economic resilience. Stay tuned for updates! https://www.rvo.nl/evenementen/economische-missie-kenia
Bioslurry Boosts Coffee Yields and Cuts Costs for Ugandan Farmers
Smallholder farmers in rural Uganda are experiencing significant benefits from using bio-slurry, an organic fertilizer derived as a by-product of biodigesters. Through the African Biodigester Component (ABC) program, these farmers are gaining valuable knowledge on the effective application of bio-slurry, which is enhancing soil fertility and improving crop yields through sustainable agricultural practices. Biomass Research is leading the Organic Fertiliser Valorisation Implementer (OFVI) project that is collecting and evaluating impacts of bio- slurry and compost on crop yields and soil health. https://www.ofvi-abc.nl/
One coffee farmer shared his success story, stating, “Using bioslurry as an organic fertilizer rejuvenated my coffee plantation and helped me cut my input costs by 50 percent.” This remarkable cost reduction allows farmers to reinvest savings into other aspects of their farms, contributing to overall agricultural sustainability and economic stability.
With the growing awareness of bio-slurry’s advantages, Ugandan farmers are increasingly embracing this organic fertilizer as a key component in their farming practices, ensuring healthier crops and a more sustainable future. https://x.com/SNVinUganda/status/1880293291788497011?t=dUNHf-JXhAQdKf_0ehRqXQ&s=03
21/05/2024 Presentation on evaluating and improving circular bioeconomies in cities and regions
European cities can become circular bioeconomy hubs, in which sustainable bio-based produced are made from biowaste. However, few cities and regions have bio-based economy strategies and projects. The HOOP project aims to further innovation in the sector by working with eight lighthouse cities and regions to implement circular processes. The projects supports cities and regions by addressing legal, financial, and technical barriers and works to unlock investments in biowaste and wastewater valorisation technologies.
In this webinar series experts from the HOOP project share learnings and best practices to help make urban circular bioeconomy projects a reality.
In this presentation, Research4Life showed research results : an inventory of biowaste and Urban Waste Sludge (UWWS) streams in eight cities and regions, from collection, to treatment, and to post-treatment utilization. The outcome of the research allows cities to evaluate current waste management and to find solutions for novel circular processes from there. Find out more about Research4Life’s outputs for the HOOP project : https://biomassresearch.eu/hoop/ and find the presentation slides on our publications page.
Biomass plays a role in the transition to a carbon-neutral economy in The Netherlands
The article, written by Sasja Hooijschuur and published in a recent issue of the Dutch journal Vakblad Energie en Duurzaamheid, examines the role of biomass in the Dutch energy mix, its primary sources, and future durability.
Biomass represents 40% of the Dutch final renewable energy consumption and is sourced primarily from waste streams. Sustainability of biomass use depends on its use as renewable energy remaining secondary to its use for primary uses (food and construction, among others), on recuperation of CO2 during combustion, and sustainability of biomass sourcing. Biomass demand will increase in the Netherlands, and is currently and predicted in the future to be a major portion of the renewable energy mix, due to affordability and versatile uses. Data in this article were sourced from the 2022 PBE report, published by Biomass Research, downloadable here: https://biomassresearch.eu/publications/
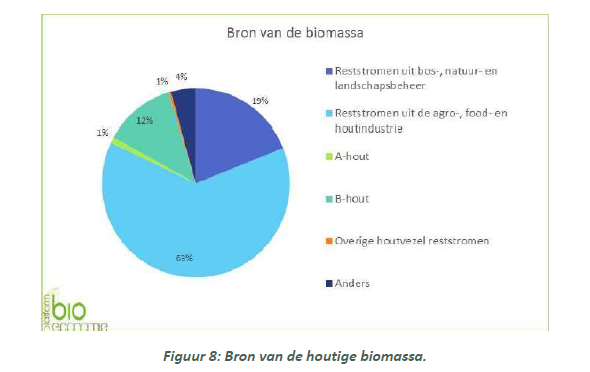
Figure sourced from the 2023 PBE report
United-States corn ethanol paper downloaded 1000 times
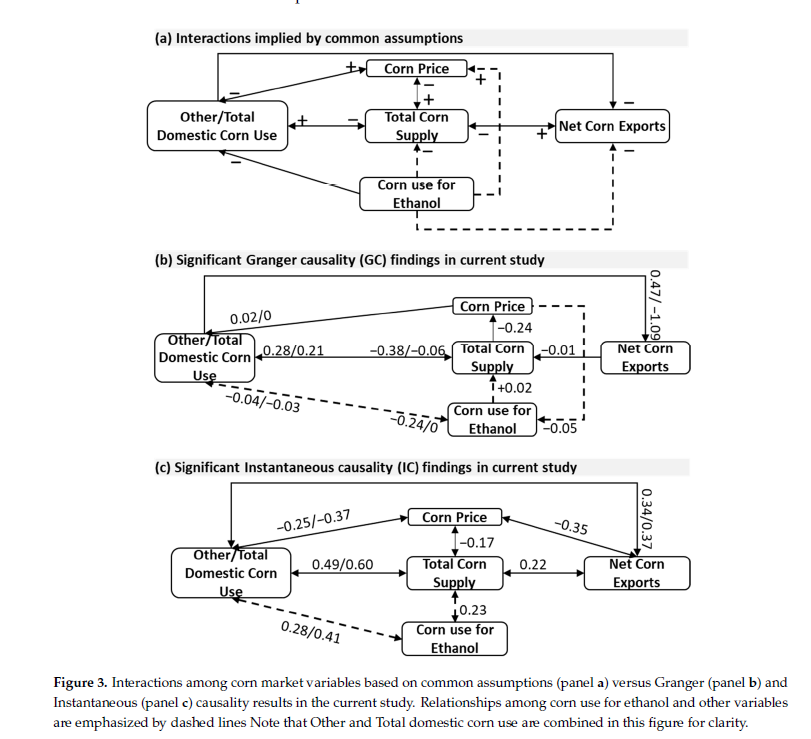
The 2021 Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) paper on United-States use of corn for ethanol has been downloaded from the Biomass Research website more than 1000 times! The authors examine causal interactions among corn market variables. The paper questions the causal relationship between increased US biofuel production from corn and rising corn and food prices globally which had been hypothesized in previous studies, showing that no causality was found. The paper concludes that linking U.S. corn ethanol production to large reductions in corn availability and exports, and higher global corn prices requires further research.
BIOMOB conference 2024: Debunking old biofuel issues
Recent targets for biokerosine (Sustainable Aviation Fuels) have sparked the discussion on the sustainability of biofuels. In a recent presentation, Hans Langeveld (director of Biomass Research) debunked two central issues : the food VS fuels, and indirect land use change (ILUC). Hans used UN statistics on hunger and food trade to demonstrate increased U.S. ethanol fuel production did not cause malnutrition or deforestation.
View the presentation on our publications page !